| Higher biological effect of light generated through | Lower biological effect of light generated through |
| Higher irradiance | Lower irradiance |
| Longer period of exposure | Shorter period of exposure |
| Higher blue share | Lower blue share |
| Wide-area light | Spotlight |
| Dynamic light changes | Constant light |
| Lower irradiance before the observed exposure to light** | |
| Light in the morning is most effective for synchronising our internal clock | Light in the afternoon has less of an effect on our internal clock |
| ** People who have adjusted to the dark for a long period of time before exposure to light are more sensitive to light and react more strongly | |
Ref.: DIN SPEC 67600
» Click here to download the Human Centric Lighting (HCL) guideline from licht.de.
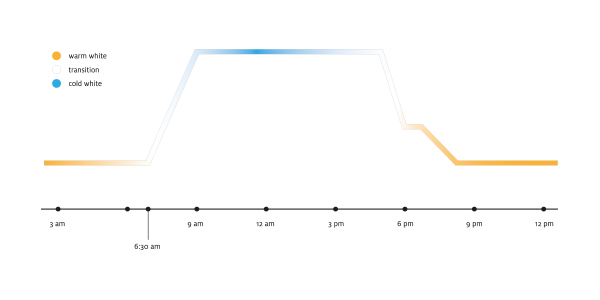
In order to be able to implement HCL-compliant planning, Zumtobel provides data sheets on "Melanopic LED effect factors" for all Zumtobel tunableWhite products.
The specified melanopic effect factors allow the lighting designer to convert photopic (visual) into melanopic (biological) evaluation parameters. Thus, the lighting designer by further calculations can make statements regarding biological effectiveness (according to CIE S 026 / E: 2018, DIN SPEC 5031-100, DIN SPEC 67600 and WELL Building Standard) of a corresponding lighting solution. Under the aspects of "Human Centric Lighting" and "Human Centered Design", these advanced planning parameters are becoming increasingly important for optimized light quality and well-being.
Exemplary: Melanopic datasheet for LIGHT FIELDS III